Introduction
Enamel hypoplasia is a dental condition that impacts the development of tooth enamel. Understanding its significance is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health. Let’s explore what enamel hypoplasia is, how it affects your smile, and why it matters.
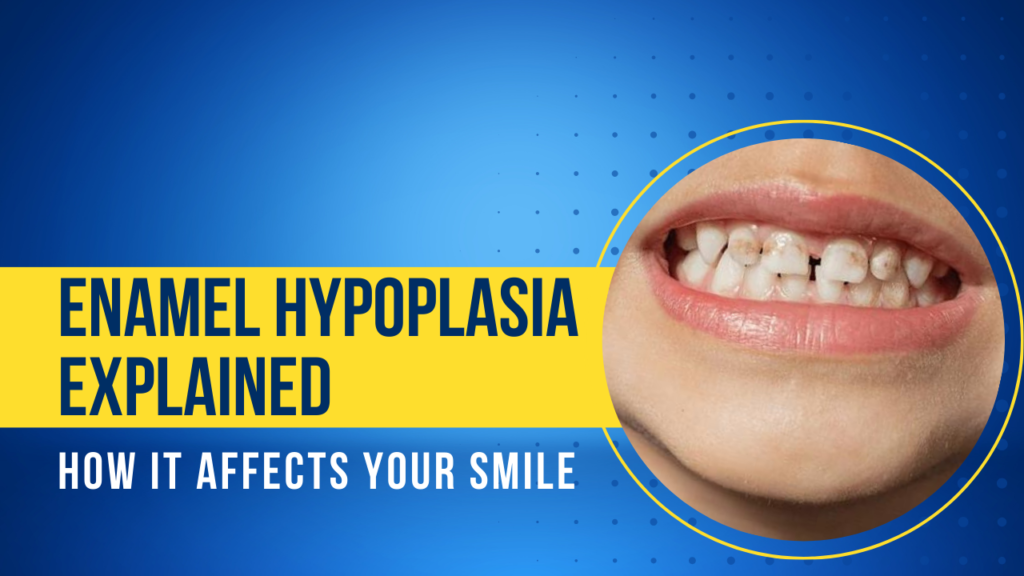
Enamel hypoplasia refers to the incomplete or deficient formation of tooth enamel during tooth development. Enamel, the outermost layer of our teeth, plays a vital role in protecting the underlying dentin and pulp. When enamel doesn’t form properly, it can lead to various dental issues.
Thin or missing enamel leaves teeth susceptible to cavities and erosion. Enamel acts as a shield against acids, bacteria, and mechanical wear. When it’s compromised, teeth become more prone to damage.Enamel hypoplasia often results in visible signs such as pits, grooves, or discoloration. These cosmetic issues can affect self-confidence and smile aesthetics.
Understanding enamel hypoplasia allows us to address it proactively and maintain healthy smiles. In the following sections, we’ll explore its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Also Read: Black Gums: What Your Oral Health Reveals
What Is Enamel Hypoplasia?
Enamel hypoplasia is a dental condition characterized by inadequate or incomplete development of tooth enamel.Enamel hypoplasia results in thin or missing enamel on specific parts of teeth.
Unlike tooth erosion (where enamel wears away over time), enamel hypoplasia involves insufficient enamel formation from the start.Tooth enamel is the hard outer layer covering our teeth, protecting the sensitive inner parts—dentin and tooth pulp.
- Role of Tooth Enamel:
- Enamel serves as a shield against mechanical wear, acids, and bacteria.
- It plays a crucial role in maintaining tooth structure and preventing damage.
- When enamel is compromised, teeth become vulnerable to decay, sensitivity, and aesthetic issues.
- Development During Tooth Formation:
- Enamel hypoplasia occurs during tooth development (both baby teeth and permanent teeth).
- Factors contributing to enamel hypoplasia include:
- Genetics: Certain genetic conditions impact enamel formation.
- Environmental Influences: Malnutrition, illness, or trauma during tooth development can disrupt enamel growth.
- Prenatal Factors: Inadequate nutrition or exposure to toxins during pregnancy may affect enamel.
- The timing of enamel hypoplasia is critical—it occurs during the enamel matrix formation stage.
- The enamel may be thin or absent on individual teeth or affect several teeth.
Also Read: Smile Studio’s Guide: How Much Is a Full Set of Dental Implants?
Causes of Enamel Hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia is a multifaceted condition influenced by both hereditary and environmental factors. Understanding these causes is essential for effective management:
1. Hereditary Factors:
Amelogenesis Imperfecta (AI):
AI is a rare genetic disorder affecting enamel formation. Individuals with AI exhibit thin, discolored enamel or even complete enamel absence.AI has various subtypes, each with distinct enamel characteristics.
Syndromes:
Certain syndromes, such as DiGeorge syndrome, can lead to enamel hypoplasia. These genetic conditions disrupt enamel formation during tooth development
Genetic Mutations:
Specific gene mutations disrupt enamel matrix proteins, impairing enamel development.
2. Environmental Influences:
Prenatal Conditions:
Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate maternal nutrition during pregnancy affects enamel formation.
Infections: Illnesses like rubella or syphilis during pregnancy can lead to enamel defects.
Premature Birth: Premature infants may experience enamel hypoplasia due to developmental challenges.
Childhood Factors:
Trauma: Dental injuries (e.g., falls) during tooth development impact enamel quality.
Infections: High fever or severe illness during early childhood affects enamel growth.
Medications: Certain antibiotics (e.g., tetracycline) taken during tooth development cause enamel discoloration.
Environmental Toxins:
Lead Exposure: Lead interferes with enamel mineralization, resulting in hypoplasia.
Fluoride Levels: Excessive fluoride during tooth development can lead to enamel defects.
Systemic Conditions:
Vitamin D Deficiency: Essential for enamel formation, lack of vitamin D affects enamel quality.
Hypoxia: Reduced oxygen supply during tooth development impacts enamel matrix production.
3. Timing Matters:
Enamel hypoplasia occurs during enamel matrix formation, which begins before birth and continues into early childhood.Identifying risk factors during these critical periods is crucial for prevention.
Also Read: Understanding the Process: Do Dental Implants Hurt?
Symptoms and Signs of Enamel Hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia manifests through various dental indicators. If you suspect enamel hypoplasia, watch out for the following signs:
- Teeth with Pits, Grooves, or Cracks:
- Enamel hypoplasia often leads to irregular surfaces on teeth.
- Look for small pits, tiny grooves, or fissures on the enamel.
- Worn-Down or Chipped Teeth:
- Insufficient enamel makes teeth more susceptible to wear and damage.
- Teeth may appear worn down or exhibit chipped edges.
- Yellowish or Brown Stains:
- Enamel thinness can result in discoloration.
- Yellowish or brown stains may be noticeable on affected teeth.
- White Spots:
- Hypoplastic areas lack enamel density, leading to white spots.
- These spots contrast with the surrounding tooth color.
- Sensitivity to Hot and Cold Foods/Drinks:
- Reduced enamel insulation exposes dentin (the layer beneath enamel).
- Sensitivity occurs when nerves react to temperature changes.
Remember that early detection allows for timely intervention. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a dentist for personalized evaluation and care.
Also Read: Decoding the Dietary Restrictions: Why No Dairy After Dental Implant?
Impact on Dental Health
Enamel hypoplasia significantly affects your oral well-being due to compromised enamel quality. Here’s a more detailed exploration:
- Increased Vulnerability to Decay:
- Thin Enamel: Hypoplastic teeth lack sufficient enamel protection.
- Cavity Risk: Reduced enamel thickness makes teeth more susceptible to cavities (tooth decay).
- Tooth Erosion: Enamel erosion occurs more readily, exposing dentin and leading to sensitivity.
- Preventive Measures: Regular dental check-ups, fluoride treatments, and proper oral hygiene are crucial to minimize decay risk.
- Uneven Tooth Surfaces:
- Pits and Grooves: Enamel hypoplasia often results in irregular tooth surfaces.
- Challenges in Cleaning: Grooves and depressions make thorough cleaning difficult.
- Plaque Accumulation: Bacteria (like plaque) adhere to these uneven surfaces, increasing the risk of decay.
- Dental Sealants: Dentists may recommend sealants to protect vulnerable areas.
- Aesthetic Concerns:
- Discoloration: Yellowish or brown stains may appear due to enamel thinness.
- White Spots: Hypoplastic areas create white spots on teeth.
- Smile Appearance: Aesthetic impact affects self-confidence.
- Cosmetic Solutions: Composite bonding or veneers can improve appearance.
Also Read: The Hidden Dangers of Dental Plaque: What You Need to Know
Diagnosis and Tests
Enamel hypoplasia can be diagnosed through the following methods:
- Clinical Examination:
- Your dental care provider will visually inspect your teeth for characteristic signs of enamel hypoplasia.
- Look out for pitted teeth, white spots, or irregular enamel surfaces.
- Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection.
- X-rays (Radiographs):
- X-rays or other imaging techniques may be used to assess the internal structure of the teeth.
- They help detect any underlying issues related to enamel development.
- X-rays are especially valuable for evaluating permanent teeth during their formation.
- Importance of Early Detection:
- Detecting enamel hypoplasia early allows for timely intervention.
- Early management can prevent further enamel damage, reduce sensitivity, and address aesthetic concerns.
- Schedule your child’s first dental visit within six months of their first tooth eruption or before their first birthday.
Also Read: Smile Makeover: Transforming Your Smile with Dental Restorations
Treatment Options for Enamel Hypoplasia
- Fluoride Treatment:
- Purpose: Fluoride strengthens weak enamel by promoting remineralization.
- How It Works: Topical fluoride applications help rebuild enamel and enhance its resistance to decay.
- Recommendation: Regular professional fluoride treatments can benefit individuals with enamel hypoplasia.
- Dental Sealants:
- Purpose: Sealants protect pits and grooves on teeth.
- Application: A thin protective coating is applied to the chewing surfaces of molars and premolars.
- Benefits: Sealants prevent food particles and bacteria from accumulating in enamel irregularities, reducing the risk of cavities.
- Composite Bonding:
- Purpose: Composite bonding addresses discolored or pitted teeth.
- Procedure: A tooth-colored resin material is applied to the affected areas.
- Result: Bonding improves aesthetics and reinforces enamel.
- Ideal for Mild Cases: Suitable when enamel defects are primarily cosmetic.
- Crowns or Veneers:
- Severe Cases: When enamel hypoplasia significantly affects tooth structure, crowns or veneers may be necessary.
- Crowns: Cover the entire tooth, providing strength and protection.
- Veneers: Thin shells placed over the front surface of teeth to enhance appearance.
- Emphasize Preventive Care:
- Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and mouthwash use.
- Professional Check-Ups: Regular dental visits for early detection and personalized guidance.
- Dietary Choices: Limit sugary and acidic foods to protect enamel.
proactive management and preventive measures play a crucial role in maintaining healthy teeth despite enamel hypoplasia.
Living With Enamel Hypoplasia
Living with enamel hypoplasia requires proactive care and awareness. Here are practical tips to manage enamel-hypoplastic teeth:
- Oral Hygiene Habits:
- Brush Twice Daily: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Brush gently to avoid further enamel wear.
- Floss Regularly: Remove plaque and food particles between teeth to maintain oral health.
- Alcohol-Free Rinses: Opt for alcohol-free mouthwashes to prevent dryness and irritation.
- Regular Dental Visits:
- Frequency: Visit your dentist every 3 months for professional cleanings and early detection of complications.
- Preventive Measures: Dentists can recommend treatments to protect your teeth and improve their appearance.
- Avoid Acidic Foods and Drinks:
- Acidic substances erode enamel. Limit consumption of:
- Citrus fruits
- Soda
- Vinegar-based foods
- Sports drinks
- Acidic substances erode enamel. Limit consumption of:
Conclusion
Enamel hypoplasia, characterized by insufficient enamel development, significantly impacts both dental aesthetics and oral health. Here’s what we’ve learned:
Thin or absent enamel leaves teeth prone to decay, erosion, and sensitivity.Pits, grooves, and irregularities affect tooth texture and cleaning.Discoloration and white spots impact smile appearance.
Seek professional advice promptly for personalized care, proactive dental care and regular check-ups are essential for managing enamel hypoplasia effectively. Your smile deserves the best care!

If you suspect enamel hypoplasia, consult our experienced dentists.From fluoride treatments to cosmetic solutions, we’ve got you covered. Reach out to Smile Studio Boston today and let us help you achieve a healthy, beautiful smile!
FAQS
1. What do teeth without enamel look like?
Teeth without enamel appear misshaped, pitted, and darker in color. They can look yellow or brown due to the exposed dentin underneath. These teeth might also show signs of wear, decay, and increased cavities due to the lack of protective enamel
2.What is enamel hypoplasia caused by a disturbance of?
Enamel hypoplasia is caused by a disturbance in the development of enamel. This can be due to genetic factors, nutritional deficiencies, illnesses during tooth development, or exposure to certain medications and chemicals.
3. Can you be born with enamel hypoplasia?
Yes, you can be born with enamel hypoplasia. It can be a congenital condition resulting from genetic factors or issues during prenatal development.
4. Does enamel hypoplasia cause pain?
Enamel hypoplasia can cause pain, particularly sensitivity to temperature changes and certain foods, due to the thin or absent enamel layer, which normally protects the nerves inside the teeth
5. What does loss of enamel feel like?
Loss of enamel can lead to increased tooth sensitivity, pain when eating or drinking hot, cold, or sweet substances, and a rough feeling on the surface of the teeth. It may also result in more cavities and visible changes in tooth appearance.
6. What does enamel hypoplasia look like?
Enamel hypoplasia typically presents as white, yellow, or brown spots on the teeth. The affected teeth may also have grooves, pits, or an uneven surface, reflecting the defective enamel formation.